Suppress, Silence, Skew and Censor
Propaganda, skewed study results and psyops, what could go wrong?
Suppressing Scientific Discourse on Vaccines? Self-perceptions of researchers and practitioners
HealthCare Ethics Committee Forum: An Interprofessional Journal on Healthcare Institutions' Ethical and Legal Issues
HEC Forum May, 2022
Abstract
The controversy over vaccines has recently intensified in the wake of the global COVID-19 pandemic, with calls from politicians, health professionals, journalists, and citizens to take harsh measures against so-called “anti-vaxxers,” while accusing them of spreading “fake news” and as such, of endangering public health. However, the issue of suppression of vaccine dissenters has rarely been studied from the point of view of those who raise concerns about vaccine safety.
The purpose of the present study was to examine the subjective perceptions of professionals (physicians, nurses, researchers) involved with vaccines through practice and/or research and who take a critical view on vaccines, about what they perceive as the suppression of dissent in the field of vaccines, their response to it, and its potential implications on science and medicine.
Respondents reported being subjected to a variety of censorship and suppression tactics, including the retraction of papers pointing to vaccine safety problems, negative publicity, difficulty in obtaining research funding, calls for dismissal, summonses to official hearings, suspension of medical licenses, and self-censorship.
Respondents also reported on what has been termed a “backfire effect” – a counter-reaction that draws more attention to the opponents’ position.
Suppression of dissent impairs scientific discourse and research practice while creating the false impression of scientific consensus.
Findings
Study participants reported being subjected to a variety of tactics perceived by them as intended to suppress, silence, and censor them due to their critical and sometimes oppositional position on vaccines. The main suppression tactics as perceived and reported by these researchers and doctors include publication of defamatory statements against them, paper retractions, denial of research grants, calls for dismissal and in some cases, summonses to hearings, suspension of their medical license by the country’s Ministry of Health, and self-censorship (refraining from expressing critical opinions about vaccines for fear of the repercussions). Family doctors (GPs) and nurses also reported pressure from the Ministry of Health to vaccinate patients.
Reading this paper brought tears to my eyes. I and others are getting hammered from all sides in this fight - including a lot of clearly controlled opposition, who are being sponsored to “attack from within” via government, advertising $$$, clicks and media fame. There are also more and more false-flag psyop campaigns that are being pushed into social media. Alternative media is under attack by what appears to be “friendly” fire, but is probably an effort by government to interject doubt into groups that they disapprove of - such as those that questions the safety and efficacy of the mRNA vaccines. In any case, those of us on the front lines are under constant stress.
The government has all the resources in the world. This truly is psychological asymmetric warfare by our government against scientists and healthcare workers who don’t comply with their narrative.
Examples of Outcome Reporting Bias in Vaccine Studies: Illustrating How Perpetuating Medical Consensus Can Impede Progress in Public Health
Cureus, Sept 21, 2022
Abstract
Introduction: Outcome reporting bias in vaccine studies is a widespread problem among all researchers who have a tendency to report selective results and conclusions that support their beliefs and values or those of sponsoring agencies. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, this bias surfaced through the unprecedented proliferation of conflicting vaccine studies. Many researchers strongly recommend and report on the safety and effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine. Those researchers who embrace the COVID-19 vaccine and vaccines, in general, are often dismissive of other researchers who present views that differ from medical orthodoxy and oppose medical consensus.
Methods: The aim of this analysis is to critically evaluate seven vaccine studies using qualitative and/or quantitative approaches to identify outcome reporting bias and assess its potential impact on the stated conclusions that align with medical consensus. Four studies claim to have found no association between autism and (a) blood levels of mercury, (b) measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine, and (c) thimerosal-containing vaccines. Three other studies claim no association exists between infant mortality rate and the number of vaccine doses, universal varicella vaccination and herpes zoster, and pandemic influenza vaccines and fetal losses.
Results: The presence of outcome reporting bias and independent reanalysis demonstrated an impact on both the direction and magnitude of the observed effect - raising questions concerning the robustness of the original study design and conclusions and challenging the current medical consensus. Medical consensus has exonerated vaccines as having any causal relationship to autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), yet no other reasonable cause has been proposed. Medical consensus attributes significant ASD increases to better case ascertainment and broadened clinical diagnosis. According to 2018 data, an estimated 1 in 44 eight-year-olds has been identified with ASD. From 1990 to 2019, there have been an estimated two million new cases of ASD in the US, with lifetime social costs exceeding $7 trillion (in 2019 dollars). Can perpetuating medical consensus impede the advancement of public health? Or has it already done so?
Conclusions
This study examined several examples of outcome-reporting biases that are found in many vaccine studies. Conflicts of interest (e.g., financial) that abound between the FDA, CDC (or foreign entities such as the Danish Staten Serum Institut), and the pharmaceutical industry impact what is ultimately reckoned as medical orthodoxy or scientific consensus.
Moreover, regulatory agencies seemingly attempt to control the narrative that vaccines are "safe and effective" through their funding or sponsorship of selective studies that often lack data transparency and, in some cases, cross bioethical boundaries.
Where vaccine study data are available, independent researchers experience an astonishing level of censorship by medical journal editors who deny publication when outcome reporting bias in the original published studies is exposed and reanalysis leads to conclusions contrary to the medical consensus.
This conduct, as well as the outcome reporting bias that is inherent to all researchers to some degree, obscures medical and scientific truth.
Ideally, if conflicts of interest could be eliminated among vaccine study sponsors, regulatory agencies, and the pharmaceutical industry, the fact that various researchers might obtain contradictory results and conclusions would not be worrisome. It may be the case that two contradictory presentations - the one supporting the medical consensus and the one that is antagonistic - may both be flawed!
Advancement of public health requires that researchers have integrity and an openness and willingness to collaborate to resolve contradictory or mixed results. In fact, it is usually through meticulous, rigorous, scientific investigation of contradictory findings that medical science has advanced and contributed to improvements in public health - since medical consensus and orthodoxy can be incorrect. The narrative that COVID-19 vaccines are "safe and effective" is not immune to outcome reporting bias. Those in support of medical consensus lose credibility and ultimately undermine public confidence in vaccine programs by censoring researchers reporting deleterious effects, especially when the numbers of adverse reactions become so prevalent that the medical community can no longer claim they are coincidental or when a given vaccine's risk-benefit ratio is shown to be no longer favorable.
Another paper on the dangers of myocarditis -
Outcomes at least 90 days since onset of myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in adolescents and young adults in the USA: a follow-up surveillance study
The Lancet, September 21, 2022
Findings
Between Aug 24, 2021, and Jan 12, 2022, we collected data for 519 (62%) of 836 eligible patients who were at least 90 days post-myocarditis onset:
126 patients via patient survey only, 162 patients via health-care provider survey only, and 231 patients via both surveys. Median patient age was 17 years (IQR 15–22); 457 (88%) patients were male and 61 (12%) were female. 320 (81%) of 393 patients with a health-care provider assessment were considered recovered from myocarditis by their health-care provider, although at the last health-care provider follow-up,
104 (26%) of 393 patients were prescribed daily medication related to myocarditis.
Of 249 individuals who completed the quality-of-life portion of the patient survey,
four (2%) reported problems with self-care,
13 (5%) with mobility,
49 (20%) with performing usual activities,
74 (30%) with pain, and
114 (46%) with depression.
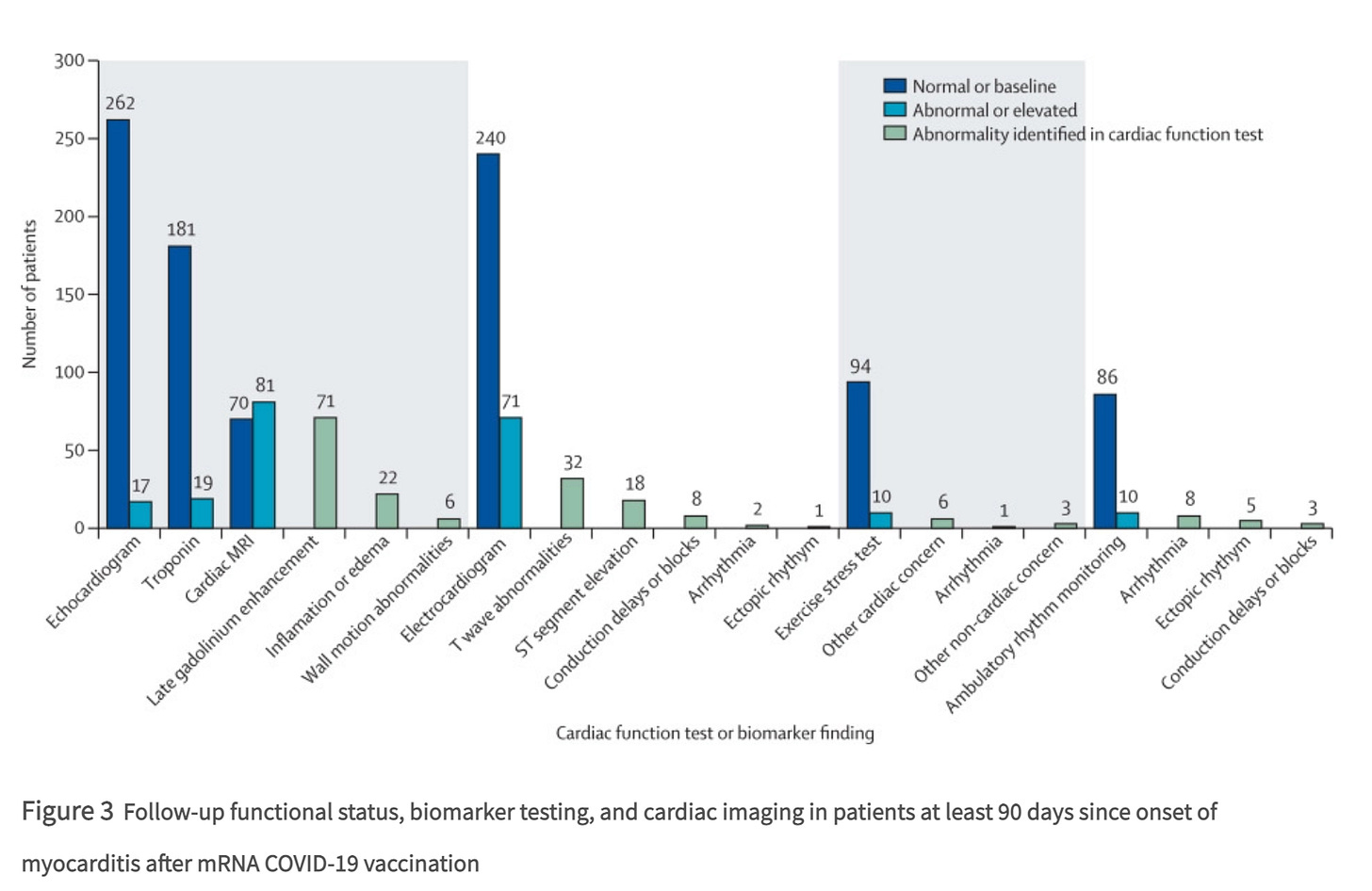
Most patients had improvements in cardiac diagnostic marker and testing data at follow-up, including normal or back-to-baseline troponin concentrations (181 [91%] of 200 patients with available data), echocardiograms (262 [94%] of 279 patients), electrocardiograms (240 [77%] of 311 patients), exercise stress testing (94 [90%] of 104 patients), and ambulatory rhythm monitoring (86 [90%] of 96 patients).
An abnormality was noted among 81 (54%) of 151 patients with follow-up cardiac MRI; however, evidence of myocarditis suggested by the presence of both late gadolinium enhancement and edema on cardiac MRI was 13% of 151 patients. As noted in the paper, there are no standard criteria for myocarditis recovery, and the authors did not identify any clinical feature or diagnostic test results associated with recovery status in the patients they evaluated.
What does this actually translate to?
When all is said and done, 90 days plus follow-up documented more than half of those participating in a VAERS database followup has an abnormal cardiac MRI and 30% had an abnormal electrocardiogram. The majority of participants did not receive a full work up -and so status is unknown for most of the tests listed.
This paper is highly artificial because it is not a true indicator of the risks and outcomes, as it is relying on the self-reporting VAERS system and then it is a survey type study only of those who have self or physician reported. Voluntary surveys data on top of voluntary self-reporting… Both of which survey designs are known for both skewing and reporting errors.
As noted in the paper, there are no standard criteria for myocarditis recovery, so these test results are to some extent, subjective.
However, even within these limitations, the data suggests that a large portion of young adults who developed myocarditis are not fully recovered at 3 months, if one accepts the abnormal cardiac MRI as criteria for not being fully recovered and if one abnormal electrocardiogram, about 30% are not fully recovered.
Heart muscle does not heal easily. Cardiac scar tissue does not dissipate easily.
The study spins these results as a kind of “good news” story. Personally, I find very little good news in these results. Nineteen percent of the patients were not considered recovered by their last follow-up with a health care provider. That is not good news.
Another example of the development and deployment of psy-ops and nudge technology during the COVIDcrisis involves messaging designed to address “vaccine hesitancy”. Even though the testing of the vaccine products were highly abbreviated and did not meet regulatory norms for either vaccines or genetic therapies, the development and clinical testing of psy-ops and nudge messaging were carefully performed using a prospective randomized, controlled clinical trial structure with short term, three and six month follow up.
Please keep in mind, these “vaccines” are unlicensed medical products available under Emergency Use Authorization. This Yale study is designed to entice and force uptake and acceptance of an unlicensed medical product without full informed consent. This is explicitly prohibited by modern international agreements concerning medical ethics.
During July of 2020, Yale University initiated a clinical trial (#NCT04460703) to develop and optimize means to psychologically manipulate people to overcome “vaccine hesitancy” to the COVID genetic vaccines via message control and content. This interventional clinical trial, entitled “Persuasive Messages for COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake: a Randomized Controlled Trial, Part 1” enrolled 4000 human subjects aged 18 and older, and was designed to assess one primary and four secondary endpoints. Although the sources of funding for most clinical trials of this size and complexity are usually clearly stated, in the case of this study the funding sources have been carefully hidden behind a veil of academic research institutes which do not disclose their sources of funding, which is also highly unusual. The sources of support listed in the final publication summarizing study results are the Tobin Center for Economic Policy at Yale University, the Yale Institute for Global Health, and the Institution for Social and Policy Studies and the Center for the Study of American Politics at Yale University. None of which state their funding sources on the publicly available web pages.
This study tested different messages about vaccinating against COVID-19. Participants were randomized to 1 of 12 arms, with one control arm and one baseline arm. The study was designed to compare the reported willingness to get a COVID-19 vaccine at 3 and 6 months of it becoming available between the 10 intervention arms to the 2 control arms.
The Primary outcome endpoint was self-reported intention to get COVID-19 vaccine immediately after the intervention message, and of the likelihood of getting a COVID-19 vaccination within 3 months and then 6 months of it becoming available.
Secondary Outcome Measures included:
Vaccine confidence scale using a validated scale to assess the impact of the messages on vaccine confidence.
Persuade others. This is a measure of a willingness to persuade others to take the COVID-19 vaccine.
Fear of those who have not been vaccinated. This is a measure of a comfort with an unvaccinated individual visiting an elderly friend after a vaccine becomes available.
Social judgment of those who do not vaccinate.
A group of different messages were tested to determine which would be the most effective for achieving primary and secondary outcomes. In other words, specific propaganda messaging was experimentally tested, conclusions drawn, and then these results were used to guide the subsequent federal US (and global) propaganda campaign to promote uptake of a poorly tested, unlicensed, experimental use authorized medical procedure and product.
The experimental messages which were tested included the following, each of which are familiar to all who were subjected to the subsequent propaganda campaign.
1) Personal freedom message: How COVID-19 is limiting people's personal freedom and by working together to get enough people vaccinated society can preserve its personal freedom. The specific message tested was as follows: “COVID-19 is limiting many people’s ability to live their lives as they see fit. People have had to cancel weddings, not attend funerals, and halt other activities that are important in their daily lives. On top of this, government policies to prevent the spread of COVID-19 limit our freedom of association and movement. Remember, each person who gets vaccinated reduces the chance that we lose our freedoms or government lockdowns return. While you can’t do it alone, we can all keep our freedom by getting vaccinated.”
2) Economic freedom message: How COVID-19 is limiting peoples's economic freedom and by working together to get enough people vaccinated society can preserve its economic freedom. “COVID-19 is limiting many people’s ability to continue to work and provide for their families. People have lost their jobs, had their hours cut, and lost out on job opportunities because companies aren’t hiring. On top of this, government policies to prevent the spread of COVID-19 have stopped businesses from opening up. Remember, each person who gets vaccinated reduces the chance that we lose our freedoms or government lockdowns return. While you can’t do it alone, we can all keep our ability to work and earn a living by getting vaccinated.”
3) Self-interest message: COVID-19 presents a real danger to one's health, even if one is young and healthy. Getting vaccinated against COVID-19 is the best way to prevent oneself from getting sick. “Stopping COVID-19 is important because it reduces the risk that you could get sick and die. COVID-19 kills people of all ages, and even for those who are young and healthy, there is a risk of death or long-term disability. Remember, getting vaccinated against COVID-19 is the single best way to protect yourself from getting sick.”
4) Community interest message: A message about the dangers of COVID-19 to the health of loved ones. The more people who get vaccinated against COVID-19, the lower the risk that one's loved ones will get sick. Society must work together and all get vaccinated. “Stopping COVID-19 is important because it reduces the risk that members of your family and community could get sick and die. COVID-19 kills people of all ages, and even for those who are young and healthy, there is a risk of death or long-term disability. Remember, every person who gets vaccinated reduces the risk that people you care about get sick. While you can’t do it alone, we can all protect every-one by working together and getting vaccinated.”
5) Economic benefit message: A message about how COVID-19 is wreaking havoc on the economy and the only way to strengthen the economy is to work together to get enough people vaccinated. “COVID-19 is limiting many people’s ability to continue to work and provide for their families. People have lost their jobs, had their hours cut, and lost out on job opportunities because companies aren’t hiring. On top of this, government policies to prevent the spread of COVID-19 have stopped businesses from opening up. Remember, each person who gets vaccinated reduces the chance that we lose our freedoms or government lockdowns return. While you can’t do it alone, we can all keep our ability to work and earn a living by getting vaccinated.”
6) Guilt message: About the danger that COVID-19 presents to the health of one's family and community. The best way to protect them is by getting vaccinated and society must work together to get enough people vaccinated. Then it asks the participant to imagine the guilt they will feel if they don't get vaccinated and spread the disease. Message 3) + “Imagine how guilty you will feel if you choose not to get vaccinated and spread COVID-19 to someone you care about.”
7) Embarrassment message: The danger that COVID-19 presents to the health of one's family and community. The best way to protect them is by getting vaccinated and by working together to make sure that enough people get vaccinated. Then it asks the participant to imagine the embarrassment they will feel if they don't get vaccinated and spread the disease. Message 3) + “Imagine how embarrassed and ashamed you will be if you choose not to get vaccinated and spread COVID-19 to someone you care about.”
8) Anger message: The message is about the danger that COVID-19 presents to the health of one's family and community. The best way to protect them is by getting vaccinated and by working together to make sure that enough people get vaccinated. Then it asks the participant to imagine the anger they will feel if they don't get vaccinated and spread the disease. Message 3) + “Imagine how angry you will be if you choose not to get vaccinated and spread COVID-19 to someone you care about.”
9) Trust in science message: A message about how getting vaccinated against COVID-19 is the most effective way of protecting one's community. Vaccination is backed by science. If one doesn't get vaccinated that means that one doesn't understand how infections are spread or who ignores science. “Getting vaccinated against COVID-19 is the most effective means of protecting your community. The only way we can beat COVID-19 is by following scientific approaches, such as vaccination. Prominent scientists believe that once available, vaccines will be the most effective tool to stop the spread of COVID-19. The people who reject getting vaccinated are typically ignorant or confused about the science. Not getting vaccinated will show people that you are probably the sort of person who doesn’t understand how infection spreads and who ignores or are confused about science.”
10) Not bravery message: A message which describes how firefighters, doctors, and front line medical workers are brave. Those who choose not to get vaccinated against COVID-19 are not brave. “Soldiers, fire-fighters, EMTs, and doctors are putting their lives on the line to serve others during the COVID-19 outbreak. That's bravery. But people who refuse to get vaccinated against COVID-19 when there is a vaccine available because they don't think they will get sick or aren't worried about it aren't brave, they are reckless. By not getting vaccinated, you risk the health of your family, friends, and community. There is nothing attractive and independent-minded about ignoring public health guidance to get the COVID-19 vaccine. Not getting the vaccine when it becomes available means you risk the health of others. To show strength get the vaccine so you don't get sick and take resources from other people who need them more, or risk spreading the disease to those who are at risk, some of whom can’t get a vaccine. Getting a vaccine may be inconvenient, but it works.”
The final peer reviewed scientific article summarizing the findings of this prospective randomized clinical trial can be found here.
Abstract
Widespread vaccination remains the best option for controlling the spread of COVID-19 and ending the pandemic. Despite the considerable disruption the virus has caused to people’s lives, many people are still hesitant to receive a vaccine. Without high rates of uptake, however, the pandemic is likely to be prolonged. Here we use two survey experiments to study how persuasive messaging affects COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. In the first experiment, we test a large number of treatment messages. One subgroup of messages draws on the idea that mass vaccination is a collective action problem and highlighting the prosocial benefit of vaccination or the reputational costs that one might incur if one chooses not to vaccinate. Another subgroup of messages built on contemporary concerns about the pandemic, like issues of restricting personal freedom or economic security. We find that persuasive messaging that invokes prosocial vaccination and social image concerns is effective at increasing intended uptake and also the willingness to persuade others and judgments of non-vaccinators. We replicate this result on a nationally representative sample of Americans and observe that prosocial messaging is robust across subgroups, including those who are most hesitant about vaccines generally. The experiments demonstrate how persuasive messaging can induce individuals to be more likely to vaccinate and also create spillover effects to persuade others to do so as well.
Discussion
Overall, the results point both to a set of effective messages and the potential efficacy of specific messages for some particular subgroups. On average, a simple informational intervention is effective, but it is even more effective to add language framing vaccine uptake as protecting others and as a cooperative action. Not only does emphasizing that vaccination is a prosocial action increase uptake, but it also increases people’s willingness to pressure others to do so, both by direct persuasion and negative judgment of non-vaccinators. The latter social pressure effects may be enhanced by highlighting how embarrassing it would be to infect someone else after failing to vaccinate. The Not Bravery and Trust in Science messages had substantial effects on other regarding outcomes and for some subgroups, but do not appear to be as effective as the Community Interest messages in promoting own vaccination behavior. Importantly, in distinct samples fielded several months apart, the Community Interest, Community Interest + Embarrassment, and the Not Bravery messages produced substantively meaningful increases for all outcomes measures relative to the untreated control, and in some instances did so in comparison to the Baseline information condition.
Our findings are consistent with the idea that vaccination is often treated as a social contract in which people are expected to vaccinate and those who do not are sanctioned. In addition to messages emphasizing the prosocial element of vaccination, we observed that messages that invoked reputational concerns were successful at altering judgment of those who would free ride on the contributions of others. This work could also help explain why social norm effects appear to overwhelm the incentive to free ride when vaccination rates are higher. That is, messages that increased intentions to vaccinate also increased the moralization of non-vaccinators suggesting that they are fundamentally linked to one another. These messages will need to be adapted in specific cultural contexts with relevant partners, such as community leaders.
The robust effect of the Community Interest message advances our current understanding of whether public health messaging that deploys prosocial concerns could be effective at increasing COVID-19 vaccine uptake. The results of both experiments presented here support prior work that demonstrated the effectiveness of communication that explains herd immunity on promoting vaccination. It also suggests that a detailed explanation of herd immunity may not be necessary to induce prosocial behavior.
Beyond the theoretical contribution, the results have practical implications for vaccine communication strategies for increasing COVID-19 vaccine acceptance. We identified multiple effective messages that provide several evidence-based options to immunization programs as they develop their vaccine communication strategies. Importantly, the insights into differential effectiveness of various messages by subgroup (e.g. men vs women) could inform messaging targeted to specific groups. Understanding heterogeneous treatment effects and the mechanisms that cause differential responses to persuasive messaging strategies requires additional testing and theoretical development. We view this as a promising avenue for future work.
Hopefully these papers will help dispel some of the confusion and controversies that are currently circulating. We have all been psychologically manipulated. Intentionally. To accept an unlicensed, poorly tested, medical product which is neither safe nor effective under any definition of effectiveness as a vaccine.
Just in case any still have any illusions about the population (including the medical community) having been subjected to a focused, planned, and field tested psy-ops campaign designed to promote compliance - and mass formation (or mass psychosis).
Further recommended reading on this topic:
COVID and mass formation psychosis (Part I)
Covidianism and the frightened crowd (Part II)
Deprogramming Covidian mass psychosis (Part III)
The Psychology of Totalitarianism
Group Psychology and the Analysis of the Ego
The Origins Of Totalitarianism
The Crowd: A Study of the Popular Mind




The Emergency Use Authorization is especially pernicious because “For FDA to issue an EUA (emergency use authorization), there must be no adequate, approved, and available alternative to the candidate product for diagnosing, preventing, or treating the disease or condition. . .”
Ergo, if any FDA-approved drug like hydroxychloroquine (or ivermectin) proved effective against covid, pharmaceutical companies would no longer be legally allowed to fast-track their zero-liability billion-dollar vaccines to market under Emergency Use Authorization. Instead, vaccines would have to go through the methodical, years-long process that all new vaccines undergo to ensure safety and efficacy, and that would mean less profits, more doubts, increased impediments to market, and potentially missing out on the unprecedented windfall that Big Pharma is currently enjoying.
Fauci invested $6 billion in taxpayer money in the Moderna vaccine alone. His agency is co-owner of the patent and stands to collect a fortune in royalties. At least four of his hand-picked deputies are in line to collect royalties of $150,000/year based on Moderna’s success, and that’s on top of the salaries already paid courtesy of the American people.
https://euphoricrecall.substack.com/p/how-fauci-wrecked-the-pandemic-response
"I and others are getting hammered from all sides in this fight - including a lot of clearly controlled opposition, who are being sponsored to “attack from within” via government, advertising $$$, clicks and media fame."
We know, Robert. Thank you, and please don't let the b@stards get you down.